HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
The circulatory system is a complex system in the human body that is responsible for the transport of blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other metabolic products throughout the body. This system consists of several parts, each with specific functions. The main parts of the circulatory system are:
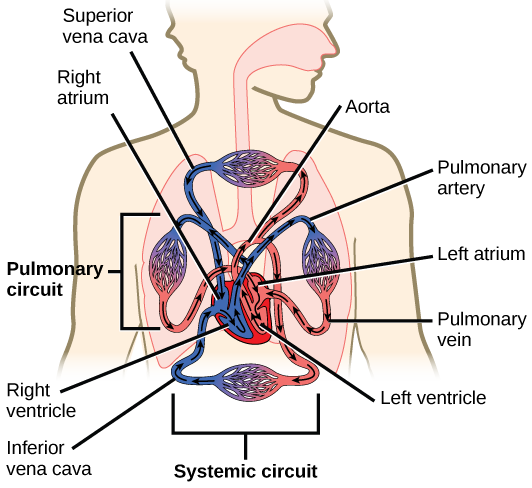
- Heart: The heart is a muscular organ that acts as a central pump in the circulatory system. Its main function is to pump blood throughout the body. It is made up of four cavities: two atria (atria) and two ventricles, which work together to maintain blood circulation.
- Blood vessels: Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body. There are three main types of blood vessels:
- Arteries: They carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the tissues and organs of the body.
- Veins: Carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries: They are very small blood vessels that allow the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste between the blood and tissue cells.
- Blood: Blood is a fluid that circulates through the circulatory system and has several essential functions:
- Transport: Brings oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes carbon dioxide and other designer products.
- Defense: Contains white blood cells that fight infections and diseases.
- Coagulation: Blood has the ability to clot to stop bleeding when an injury occurs to a blood vessel.
- Regulation: Transports hormones and regulates body temperature.
In summary, the
circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood vessels and blood, and plays
a vital role in the distribution of nutrients, oxygen and other essential
substances to the body's cells, as well as in the elimination of waste
products. . . It is also essential in the immune response and the regulation of
body temperature. The cooperation of these parts ensures the proper functioning
and homeostasis of the body.
Publicar un comentario